
- Synchronize Time With Ntp Server Password
- Synchronize Time With Ntp Server Settings
- Synchronize Time With Ntp Server Ip
- Windows Ntp Time Server Address
By default if NTP service is running it will automatically sync the client’s date and time from the NTP server based on the polling interval but what if you want to do a force sync immediately and cannot wait for the NTP client to sync it.
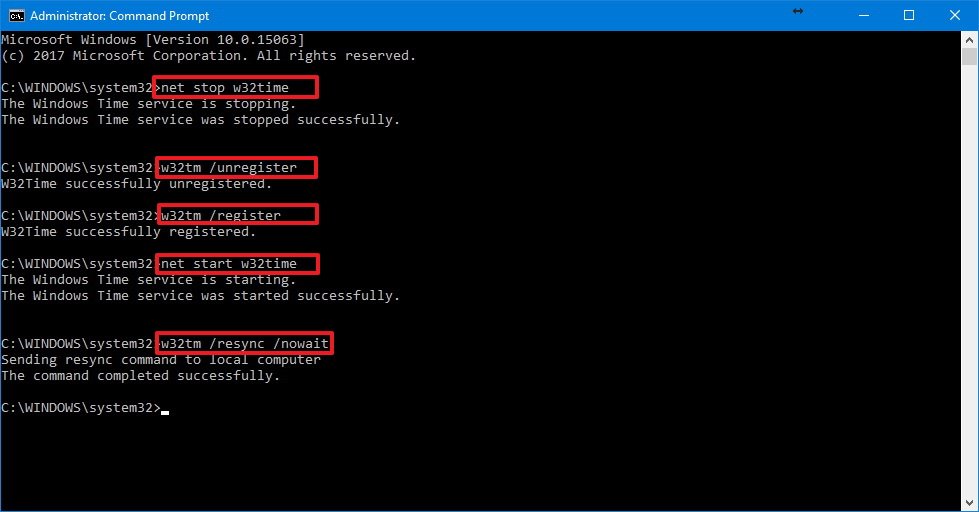
On SuSE Enterprise Linux
The current date and time on my node is
Go to the ' Time & Language → Date & Time ' page. On the right-panel, click on the ' Sync ' button under the Synchronize your clock section. As soon as you click the button, the PC will sync the time with the default Windows time server. The settings app won't allow you to change the default time server. Jul 30, 2020 The Network Time Protocol ( NTP) is a protocol used to synchronize computer system clock automatically over a networks. The machine can have the system clock use Coordinated Universal Time ( UTC) rather than local time. Maintaining accurate time on Linux systems especially servers is a important task for many reasons. Time synchronization may not succeed when you try to synchronize with a non-Windows NTP server.; 2 minutes to read; D; S; In this article. This article provides a resolution for the issue that time synchronization may not succeed when you try to synchronize with a non-Windows NTP server.
My ntp service status
# /etc/init.d/ntp statusremote refid st t when poll reach delay offset jitter
192.168.10.100 10.171.8.4 3 u 1 64 1 0.173 -593996 0.000
10.40.130.1 .INIT. 16 u – 64 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
Checking for network time protocol daemon (NTPD): running
So my ntp client is running, lets change the date and time of my node before doing a force sync
Mon Dec 4 10:00:00 IST 2017
My new date and time
Time to do a force sync
Time synchronized with 192.168.10.100
So as you see it immediately sent a request to the NTP server and updated the localhost date and time details from the NTP server
On Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7
Unfortunately ntptimeset is not available in Red Hat Enterprise Linux so we have to try something else
My existing date and time
Thu Dec 7 10:25:03 IST 2017
NTPD service status
# systemctl status ntpd● ntpd.service – Network Time Service
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/ntpd.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active
Synchronize Time With Ntp Server Password
(running) since Wed 2017-12-06 17:43:02 IST; 16h agoSynchronize Time With Ntp Server Settings
Process: 5957 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/ntpd -u ntp:ntp $OPTIONS (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 5958 (ntpd)
CGroup: /system.slice/ntpd.service
└─5958 /usr/sbin/ntpd -u ntp:ntp -g

Dec 06 17:43:02 Ban17-pgw01-a systemd[1]: Starting Network Time Service…
Dec 06 17:43:02 Ban17-pgw01-a ntpd[5957]: ntpd 4.2.6p5@1.2349-o Wed Mar 1 09:00:51 UTC 2017 (1)
Dec 06 17:43:02 Ban17-pgw01-a systemd[1]: Started Network Time Service.
Dec 06 17:43:02 Ban17-pgw01-a ntpd[5958]: proto: precision = 0.038 usec
Dec 06 17:43:02 Ban17-pgw01-a ntpd[5958]: 0.0.0.0 c01d 0d kern kernel time sync enabled
Now lets change the date and time
Mon Dec 4 10:00:00 IST 2017
First stop the ntpd service
Next initiate a force sync from your NTP server using the below command
Synchronize Time With Ntp Server Ip
7 Dec 10:27:36 ntpdate[6701]: step time server 192.168.10.100 offset 260769.003401 sec
Windows Ntp Time Server Address
Now start the NTP service again
Lastly validate if your localhost date and time is updated correctly
Thu Dec 7 10:27:48 IST 2017
when behind a firewall that blocks incoming traffic to privileged ports, and you want to
synchronize with hosts beyond the firewall. Note that the -d option always uses unprivi‐
leged ports.
Without ‘-u‘ and when NTPD service is running
10 Feb 17:34:48 ntpdate[2574]: the NTP socket is in use, exiting
With ‘-u‘ and ntpd running in the background
10 Feb 17:35:22 ntpdate[2575]: step time server 13.126.37.14 offset 1.335054 sec
I hope the article was useful.